Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, the primary source of energy for cells. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition usually develops in children and young adults. The immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in little to no insulin production. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, Type 2 diabetes typically occurs in adults, although it is increasingly seen in children and adolescents. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet significantly contribute to its development. Management may include lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
Symptoms and Complications
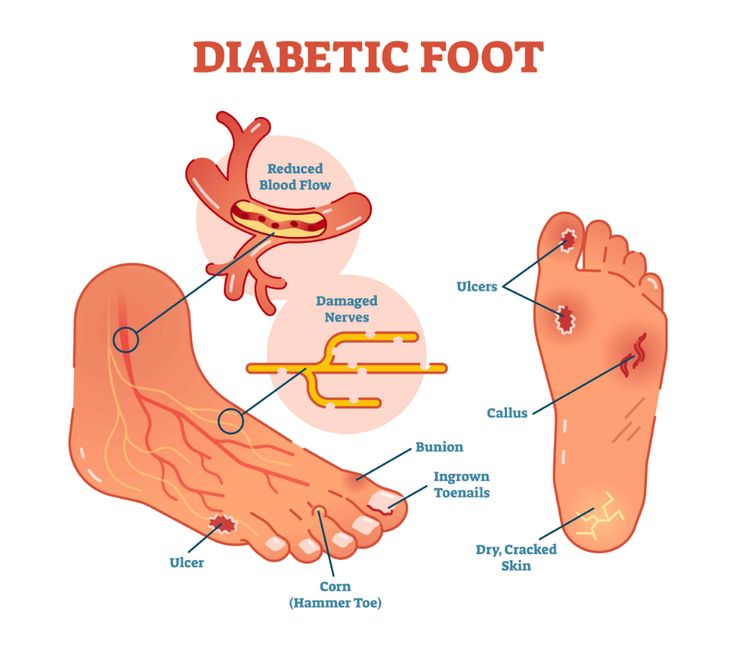
Common symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, and vision problems.

Management and Prevention
Effective management of diabetes involves regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medication adherence. Education and support are vital for individuals living with diabetes to make informed lifestyle choices.
Preventing Type 2 diabetes focuses on maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and eating a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
In summary, understanding diabetes is essential for prevention and effective management, improving the quality of life for millions of individuals affected by this condition.
4o mini
